10 Apr 2020
iOS - persistence - core data stack
Core Data Stack
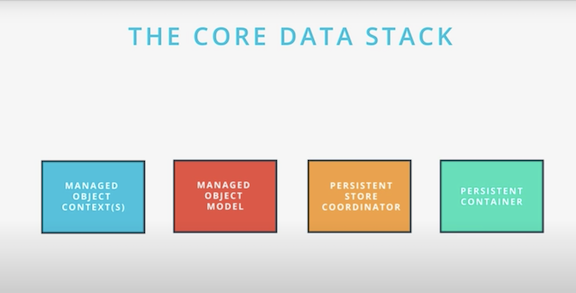
Managed Object Context
NSManagedObjectContext- an intelligent scratch pad for working with managed objects
- associate or register it with a context. Never instantiate directly

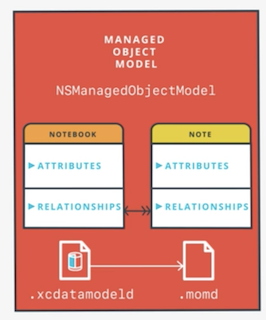
Managed Object Model
NSManagedObjectModel- a description of the app’s data, including entities, attributes, relationships, and class mappings
Persistent Store Coordinator
NSPersistenceStoreCoordinator- a mediator for turning persisted data into managed objects and turning managed objects into persisted data
- interfaces with the underlying persistent store, such as SQL, so we don’t have to
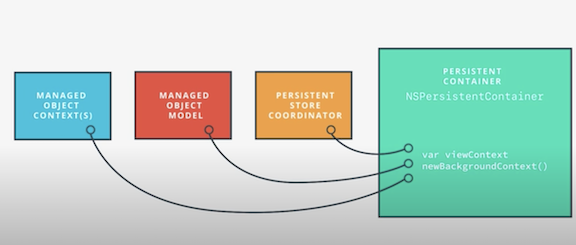
Persistent Container
NSPersistentContainer- a helper that handles creation of the stack, and provides convenience methods
Fetch Requests, Faults, and Uniquing
Fetch Requests
-
An NSFetchRequest specifies the criteria needed to select and optionally sort a group of managed objects held in a persistent store.
- Do not want to fetch all the data at once. Ideal to make multiple requests to get the data you need because iOS devices have finite memory, apps can have a lot of data, and fetch requests help limit your app’s data consumption.
- A finely-tuned fetch request means we’ll only use the minimum memory required to display content to the user.
Faults
- Relationships are not immediately loaded. Instead, Core Data has a mechanism called faulting. Faulting allows any attribute or relationship to be in a special state where it is promised to load when needed. When you fetch a managed object, its relationships are initially represented as faults.
- Core Data automatically retrieves the data either from a cache or from the persistent store
Uniquing
- Allows you to avoid reload the same object in the object belongs in several different object graphs/ relationships.
- Example: a song can belong to multiple playlists
Code Examples
You have an NSManagedObject subclass named Animal, and an NSManagedObjectContext in a local variable called context. Create a new managed object and save it in the persistent store.
class DataController {
let persistentContainer: NSPersistentContainer
var viewContext: NSManagedObjectContext {
return persistentContainer.viewContext
}
init(modelName: String) {
persistentContainer = NSPersistentContainer(name: modelName)
}
func load(completion: (() -> Void)? = nil) {
persistentContainer.loadPersistentStores { (storeDescription, error) in
guard error == nil else {
fatalError(error!.localizedDescription)
}
self.autoSaveContext()
completion?()
}
}
}
Inject DataController AppDelegate.swift
let dataController = DataController(modelName: "Animals")
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
dataController.load()
let navigationController = window?.rootViewController as! UINavigationController
let animalsViewController = navigationController.topViewController as! AnimalsViewController
animalsViewController.dataController = dataController
return true
}
Load Data via Fetch Requests
let fetchRequest: NSFetchRequest<Animal> = Animal.fetchRequest()
let sortDescriptor = NSSortDescriptor(key: "birthDate", ascending: false)
fetchRequest.sortDescriptors = [sortDescriptor]
if let result = try? dataController.viewContext.fetch(fetchRequest) {
aniamls = result
tableView.reloadData()
}
Add a new animal to the end of the animals array
func addAnimal(name: String) {
let animal = Animal(context: dataController.viewContext)
animal.name = name
animal.birthDate = Date()
try? dataController.viewContext.save()
animals.insert(animal, at: 0)
tableView.insertRows(at: [IndexPath(row: 0, section: 0)], with: .fade)
}
Delete a new animal to the end of the animals array
/// Deletes the animal at the specified index path
func deleteAnimal(at indexPath: IndexPath) {
let animalToDelete = animal(at: indexPath)
dataController.viewContext.delete(animalToDelete)
try? dataController.viewContext.save()
animals.remove(at: indexPath.row)
tableView.deleteRows(at: [indexPath], with: .fade)
}
Til next time,
lovelejess
at 10:13

